The Skin Center
Fax (949) 582-7691
Author: Dr. Nili N. Alai, M.D., FAAD
Jock Itch
What is jock itch?
Jock itch is a very common, itchy rash of the groin. It can be a very intense itch with or without a visible red or pink rash in the groin folds and genitals. Although jock itch is primarily a skin condition in men, female jock itch is much less common.
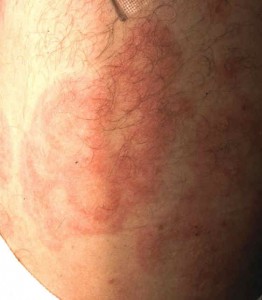
In general, jock itch tends to be a mild condition that occurs at least once at some point in most people’s lives. The symptoms may intermittently come and go and many cases of jock itch resolve spontaneously without any treatment. Jock itch is primarily seen in the groin, although it may spread to the inner thighs, genitals (including penis, scrotum, labia and vaginal opening), and anus.
While jock itch is frequently noted in otherwise healthy patients, it is more common in diabetes and/or obesity. Possible causes of this common groin itch include irritation from tight or abrasive underwear, excess moisture, sweating, skin rubbing or friction, allergic problems, fungal infection, Candida (yeast) infection, and bacterial overgrowth or skin infection. It is important to keep in mind that not all cases of jock itch are caused by fungus.
Treatment of fungal related jock itch may typically include one or a combination of antifungal shampoos to wash the groin, antifungal creams, and rarely antifungal pills. Treatment of jock itch that is not caused by fungus involves proper groin hygiene, keeping the area clean and dry, and washing frequently with gentle soap and water (especially after sweating or exercise).
What are symptoms of jock itch?
Jock itch usually begins with mild intermittent itching in the groin. The itching can get worse and become unbearable in some cases. The rash is usually on both sides of the groin and affects the folds primarily.
The rash may become dry, rough, and bumpy, develop pus bumps, or begin to ooze. Sometimes, the upper most skin clears as the rash spreads further down onto the thighs.
The itching and rash can spread to the genitals including the labia, vagina, scrotum, penis, and anus.
Women may also develop vaginal white discharge and yeast infections. Men may develop balanitis and other infections on the head of the penis, especially if they are not circumcised.
![scabies1[1]](https://lagunaskincenter.com/wp-content/uploads/scabies111-300x225.jpg)
Severe cases may be very uncomfortable and develop secondary complications like breaks in the skin, open sores, ulcers, and rarely cellulitis.
Who gets jock itch?
Jock itch is most common in adult and middle aged men. Anyone can get jock itch and it is estimated to affect nearly all people at some point in their lives.
Certain groups of people may be more prone to jock itch. Patients with diabetes, obesity, and those with a compromised immune system like in HIV/AIDS, hepatitis, chronic illnesses, cancer, systemic chemotherapy, immunosuppressive drugs like prednisone, and those on biologic immune system modifying drugs like Remicade or Enbrel may be more prone to jock itch.
Risk factors include
- Heat
- Moisture
- Humidity
- Obesity
- Excess Sweating
- Exercise
- Weakened immune system
- Tight, occlusive fabrics and undergarments
- Athlete’s foot infection or other “ringworm” on the body
What is the prognosis with jock itch?
The prognosis with jock itch is very good. Overall, jock itch tends to be an easily treated and curable skin condition. Commonly, it is a mild, benign, usually non-contagious, and self-limited skin condition. More widespread, atypical cases of jock itch may be embarrassing, chronically disfiguring, and psychologically distressing for the patient.
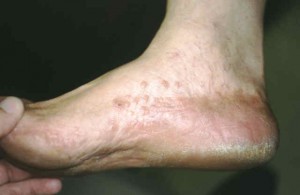
Does jock itch affect the entire body?
Jock itch does not affect the entire body. It is usually limited to the groin, inner thigh folds, genitals, and anal area. Itching of the entire body is called pruritus and is generally unrelated to jock itch.
What does jock itch look like?
Photos of jock itch patients typically show a symmetrical red or pink rash on the sides of the groin folds. There may be a dry, scaly rash or a collection of small, pinpoint red or pink bumps at each hair follicle. Sometimes, there may be no rash at all.
How is jock itch diagnosed?
The diagnosis of jock itch is typically very straightforward and based on the symptoms and skin appearance.
In some cases, a small skin biopsy may be used to help the doctor confirm the diagnosis. Other times, a skin swab or culture may be taken and sent to the lab to determine an infectious cause of the jock itch. A few other medical conditions may look just like jock itch and need to be examined more closely by a physician specializing in conditions of the skin called a dermatologist.
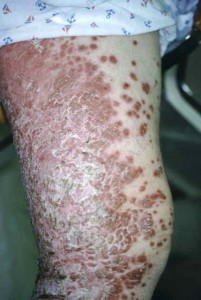
What else could jock itch look like?
Other medical conditions can mimic jock itch. Some possible look-alike skin conditions include:
- “Ringworm” also called Tinea cruris
- eczema
- intertrigo
- erythrasma
- impetigo
- atopic dermatitis
- irritant or contact dermatitis
- heat rash
- dry skin (xerosis)
- inverse psoriasis
What causes jock itch?
Jock itch is a basic problem with inflammation of the skin in the groin. This inflammation may be caused by simple irritation, infections like bacteria and yeasts, or other non-infectious skin conditions.
- Moisture, warmth, and skin friction in the groin folds
- Tight, occlusive clothing and undergarments that trap in sweat
- Contact with fungus and yeasts
- Contact with bacteria
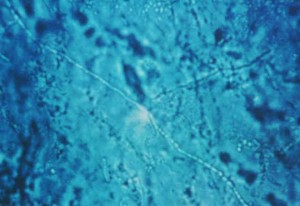
Different skin infections may include:
- Candida albicans ( yeast)
- Trichophyton (fungus)
- Epidermophyton floccosum (fungus)
Is jock itch caused by athlete’s foot?
Jock itch may be caused by athlete’s foot, also called tinea pedis. The same fungus that causes athlete’s foot in a person may actually spread over to the groin in some cases. It is important to always check the feet for rashes in persons with jock itch. Spread of the fungus usually occurs when fungal particles pass onto the crotch of the pants while actually getting dressed. Any concurrent foot infection must be treated in order to avoid recurrence of the jock itch.
Is jock itch curable?
Most cases of jock itch are easily and fully curable. There are very uncommon, long-standing cases of jock itch that may not be curable. Often these more resistant cases may be controlled with proper treatment and medication. Jock itch sometimes clears completely by itself without treatment.
Is jock itch contagious?
Although most cases of jock itch are not contagious, cases caused by an infection may be transmitted through skin or sexual contact, sharing of swimwear, or towels. It is possible to give fungal cases of jock itch to someone else through close skin contact.
Some people are simply more prone to developing jock itch because of their overall health, activity, anatomy, possible altered immune status, exposure history, and other predisposing skin conditions like eczema. Patients with athlete’s foot (tinea pedis) are more prone to developing jock itch.
What are possible complications of jock itch?
Complications are infrequent since jock itch is usually a self-limited skin condition. Rarely, the rash may spread past the groin onto the thighs and genitals. Secondary skin infections from scratching or rubbing may uncommonly deepen causing cellulitis or abscess formation.
Another potential complication includes temporary skin discoloration called post-inflammatory hypopigmentation (lighter than the regular skin color) or hyperpigmentation (darker then the regular skin color). This altered skin color may occur after the rash has improved or after a temporary flare. Permanent scarring is uncommon.
Are there any lab tests to help diagnose jock itch?
Usually, no specific laboratory tests are needed in the diagnosis of common jock itch.
Imaging studies like x-rays or CT scans are not useful.
A bacterial culture may be useful to check for bacteria like staphylococcus on the skin.
Microscopic skin tests and fungal tests using potassium hydroxide may help to determine if the jock itch is caused by yeast or a fungus.
Skin biopsy (surgically taking a small piece of skin using local numbing medicine) with histopathological (exam of tissue under the microscope) evaluation may be useful in atypical or widespread cases. Sometimes skin biopsies help to exclude other possible diagnosis.
Does diet have anything to do with jock itch?
Overall, diet does not seem to affect jock itch.
How do I treat jock itch?
There are many treatment options and skin care recipes for treating jock itch. Since the two primary causes of jock itch are excess moisture and fungal infections,
the specific treatment depends on the exact cause of the jock itch. Treatment of jock itch associated with skin irritation and excess moisture should address general measures to keep the groin clean and dry. Treatment of fungal jock itch should include antifungal creams used continuously for 2-4 weeks.
It is important to keep in mind that as with any condition, no therapy is uniformly effective in all people. Your doctor may need to help evaluate the cause of your jock itch.
What home remedy can I use for jock itch?
Home remedy for mild jock itch includes:
- Wash the groin skin 2-3 times a day with a gentle soap-less cleanser like Dove non-soap cleanser or Cetaphil and water
- Keep the groin area dry. ( A great tip is to spray a deodernat spray along the groin folds and under the scrotum)
- Avoid excess groin skin irritation by wearing 100% cotton underwear
- Avoid fabric softeners, bleaches, or harsh laundry detergents
- Use a mix of over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream and clotrimazole cream 1-2 times a day to the affected area
What holistic jock itch treatments are available?
Holistic (non-medicated) home remedy options for jock itch include:
- Soak the affected area with a washcloth dipped in dilute white vinegar (1 part vinegar to 4 parts of water) and dry the skin daily
or
- Soak in a bathtub with very dilute Clorox bleach (1 quarter cup of Clorox bleach in a bathtub full of water) and dry the skin daily or every other day
How do I treat fungal jock itch?
Mild fungal or yeast jock itch may be treated by:
- Washing groin twice daily with an antifungal shampoo like ketoconazole (Nizoral Shampoo) or selenium sulfide (Selsun Blue Shampoo)
Moderate fungal or yeast jock itch is often treated by a combination of:
- Washing groin twice daily with an antifungal shampoo like ketoconazole (Nizoral Shampoo) or selenium sulfide (Selsun Blue Shampoo)
- Topical antifungal cream like miconazole (Monistat, Micatin), clotrimazole (Lotrimin, Mycelex) or terbinafine (Lamisil)
Severe fungal or yeast jock itch is typically treated by a combination of:
- Washing groin twice daily with an antifungal shampoo like ketoconazole (Nizoral Shampoo) or selenium sulfide (Selsun Blue Shampoo)
- Topical antifungal cream like miconazole (Monistat, Micatin), clotrimazole (Lotrimin, Mycelex) or terbinafine (Lamisil)
- Antifungal pill like fluconazole (Diflucan), itraconazole (Sporanox), or terbinafine (Lamisil)
How do I treat bacterial jock itch?
Mild bacterial jock itch may be treated with:
- antibacterial skin washes like Lever 2000 soap or chlorhexidine (Hibiclens) soap twice daily
- Spray deoderant spray under groin fold area ( do not use deodernat stick because can cross contaminate and infect)
Moderate bacterial jock itch may be treated with:
- antibacterial skin washes like chlorhexidine (Hibiclens) soap twice daily
- twice-daily application of a topical antibiotic like clindamycin lotion or metronidazole lotion
Severe bacterial jock itch may be treated with:
- antibacterial skin washes like chlorhexidine (Hibiclens) soap twice daily
- twice-daily application of a topical antibiotic like clindamycin lotion or metronidazole lotion
- 5 to 14 day course of an oral antibiotic like cephalexin, dicloxacillin, doxycyline, minocycline, tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, or levofloxacin for more resistant cases.
How do I treat itching from jock itch?
Inflammatory jock itch may be treated with a short course of one of the following:
- Use a short 5-7day course of a mild to medium potency, topical steroid cream like prescription triamcinolone 0.025% once or twice a day for inflamed or itchy areas.
- Use a short 5-7day course of a mild, over-the-counter topical steroid cream like hydrocortisone (Cortaid) 1-3 times a day for itching
- Use a topical immunomodulator like pimecrolimus (Elidel) cream or tacrolimus (Protopic) ointment twice a day. Although these creams are approved for atopic dermatitis and eczema, their use would be considered “off label” (non-FDA labeled use) for jock itch.
Why is my groin still discolored?
Residual skin discoloration in the groin may persist for weeks to months after more severe forms of jock itch clear. This discoloration is called hyperpigmentation and may be treated with one or a combination of:
- hydroquinone 4% cream
- kojic acid cream
- azelaic acid 15% cream
- over the counter fading cream with 2% hydroquinone (Porcelana)
- specially designed prescription creams for particularly resistant skin discoloration using higher concentrations of hydroquinone 6%, 8%, and 10% may also be formulated by prescription by compounding pharmacists.
What is the best drug for jock itch?
Overall, the best jock itch drug is a topical antifungal cream like miconazole (Monistat, Micatin), clotrimazole (Lotrimin, Mycelex) or terbinafine (Lamisil). If the jock itch does not improve within 2-3 weeks of treatment, then a physician should be consulted.
When should I call my doctor?
If your jock itch persists over 1-2 weeks despite proper skin care and use of over-the-counter medications, you may need to schedule an appointment to see your physician. In addition, if your rash is worsening despite medical treatment or if you develop sings of an advancing skin infection, you should contact your physician.
- Spreading despite treatment
- Increasing pain
- Rapidly spreading rash
- Formation of pus, abscesses, or draining sores
- Red streak(s) extending from the groin (called lymphangitis)
- Fever or chills
- Failing to improve after 2 weeks of continuous topical treatment
How do I prevent jock itch?
Jock Itch prevention efforts include good general skin hygiene and keeping your groin clean and dry.
- Wash groin and buttocks with soap and water off after exercise and sweating
- Wash workout clothes, underwear, and swimwear after each use
- Minimize groin moisture by using white cotton underwear
- Change underwear frequently and especially after sweating
- Wash clothes and undergarments in hot soapy water

PHOTO OF:Prevention with Hand Washing and Good Hygiene - Use loose fitting cotton underwear and clothing
- Avoid undergarments with polyesters, nylon, or synthetic fibers
- Use a deodorant spray after washing and drying the groin each day
- Wash your groin well after exercise or sweating ( Sweat can have a lot of irritating salt and minerals)
- Use an antifungal powder like Lamisil or Zeasorb to keep the groin dry
- Avoid fragranced or irritating creams or lotions on the groin
- Avoid going barefoot, especially at gyms, schools, and public pools
- Treat athlete’s foot if you have it
- Cover your feet with socks before you put on your underwear and pants
Jock itch at a Glance
- Very common, itchy groin rash
- Roughly half of cases are caused by a fungus
